- Blog, Engineering & Production
- Published on: 08.05.2024
- 12:31 mins
How the Asset Administration Shell Is Shaping the Future of Digital Twins
Digital twins are revolutionizing the way organizations create, monitor, and optimize their physical assets, processes, and resources. But what makes digital twins so revolutionary, and why is it now the right time for companies to take this digital step? The key element for success is the consistent standardization of digital twins, especially with regard to the structuring of model components and interfaces. The Asset Administration Shell (AAS) offers a solution here. It ensures the standardized exchange of data and thus creates a solid basis for digitization projects.
The Asset Administration Shell for Industry 4.0: The Key for Digital Twins
In this current era, where data is so important, digital twins represent an innovative link between the physical and digital worlds. The Asset Administration Shell is a central component in the implementation of digital twins, especially within the context of the concept of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). It serves as a digital representation of a physical object or system (the “asset”) and enables seamless integration and communication between different digital and physical entities.
In this blog post, you'll learn what AAS is and how MHP can help you establish the Asset Administration Shell as the foundation for sustainability and innovation in your organization.
What Is the Asset Administration Shell?
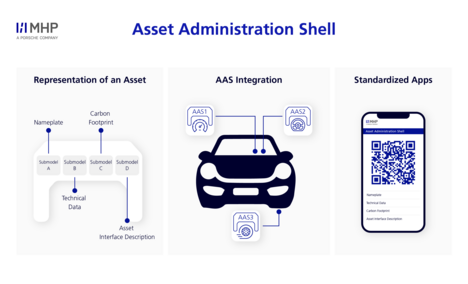
The Asset Administration Shell represents a semantic standardization of the digital twin, which can be considered as a digital representation or model of a physical and digital asset. It is divided into so-called submodels. These form the standardized components and their contents can be clearly identified.
An asset can be a single piece of production equipment, but it can also be an entire factory or plant that is fully and holistically mapped by the AAS.
AAS are based on digital images, hereinafter referred to as models, and accompany a product throughout its entire life cycle. Due to the different applications, the model is subject to different requirements. However, since it takes a great deal of resources to create a model, models, or parts of models need to be able to be reused within the product life cycle to ensure an efficient approach. The digital nameplate, for example, makes it possible to transfer basic information about a product and to make it available digitally in accordance with global labeling requirements.
Industrial Digital Twin Association (IDTA)
The Industrial Digital Twin Association (IDTA) plays a decisive role in this context. It promotes standards and best practices for the development and implementation of digital twins, including the AAS. This supports digitization efforts in industry by providing a structured and machine-readable database, and contributes to the optimization of processes, simplification of maintenance, and the creation of innovative business models.
Shaping the Future with AAS: Opportunities to Transform Your Business
Implementing the Asset Administration Shell offers numerous opportunities for your business:
Process optimization: AAS facilitates an increase in efficiency and transparency within operations by replacing the heterogeneous data landscape with a unified and interoperable data structure that allows for the integration of different IT systems.
Innovative business models: The improved availability and usability of data through AAS promotes the development of new approaches by providing a foundation for advanced analytics and data-driven decision-making.
Efficiency: AAS helps achieve precise monitoring and controlling of production processes by providing seamless communication between machines and systems. This in turn increases both profitability and competitiveness.
Sustainability: Your business can operate more sustainably by optimizing the use of resources and implementing eco-friendly practices, all supported by AAS-based data analytics.
Digital transformation: AAS serves as a key technology for transforming traditional operating models with a robust and secure data infrastructure that replaces heterogeneous data landscapes and enables a unified view of assets, asset types and instances, and resources.
Market adaptability: The flexibility of AAS allows you to quickly adapt to market changes by providing dynamic and scalable solutions for data integration and analysis, thus strengthening your company’s market position.
Integrating the Asset Administration Shell into a company’s strategic framework not only expands its capabilities in terms of optimization and innovation, but also signals a determination to focus on future viability.
Submodels: The Building Blocks of the Asset Administration Shell
Submodels are standardized, essential building blocks and are indispensable within an Asset Administration Shell. They ensure that assets and asset instances are managed efficiently and with sufficient detail.
How MHP is contributing to the development of submodels
The IDTA is the organizational unit for the publication of submodels. Here at MHP, we are involved in various working groups on the submodels. Teams of experts meet at regular intervals – typically every six to twelve months – to discuss the crucial parameters required to accurately describe each submodel. After an intensive round of discussions, the defined parameters are presented to the IDTA decision-making panel, which then carefully evaluates them. Once they have been successfully tested, the submodels are officially published and are available for use according to a defined scheme.
Submodels: Your asset, mapped perfectly
One key aspect of AAS is its ability to accommodate any number of submodels that represent specific aspects of an asset. This structured and modular approach allows for comprehensive and flexible asset management in line with the requirements of Industry 4.0.
Let’s take a battery as an example: Here, various submodels, such as the digital nameplate, the carbon footprint over the entire life cycle, technical data, and the asset interface description could all be integrated. These submodels are designed according to strict standards to ensure a consistent database with comparable data.
Access rights to the submodels can be regulated individually: While some data is publicly available, other data has limited availability. Furthermore, an AAS can also consist of several nested Asset Administration Shells and form a network of digital models.
AAS as an Enabler of the Digital Product Passport (DPP)
The Asset Administration Shell is seen as an enabler of the digital product passport (DPP). A digital product passport is a collection of information that contains details about the components, materials and chemical components of a product. It also provides information on repair options, availability of spare parts and the correct disposal of the product. This information covers the entire life cycle of the product – from the design phase to disposal.
The AAS plays a key role in this – it serves as a digital and logical representation of a physical asset and enables the structured collection, storage, and exchange of this information. Here are some of the reasons as to why the AAS acts as an enabler for the digital product passport:
1. Standardized information structure
The AAS provides a standardized structure to organize and provide access to information about products and equipment. This facilitates the integration and exchange of data between different stakeholders along the value chain and across different stages of the product life cycle.
2. Interoperability
AAS uses standardized models and interfaces and so improves interoperability between different IT systems and platforms. This enables a seamless exchange of information between manufacturers, suppliers, customers and recycling companies.
3. Transparency and traceability
The AAS enables detailed documentation and traceability of product information, which is essential for transparency throughout the entire life cycle of a product. This not only supports sustainability initiatives, but also compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. Supporting sustainability objectives
The digital product passport is an important tool for achieving sustainability goals, as it provides detailed information about a product’s environmental impact. The AAS facilitates the collection and provision of this information, which helps companies make more sustainable choices.
5. Flexibility and expandability
The modular nature of AAS makes it possible to define specific submodels for different aspects of a product or asset – including those relevant to the digital product passport. The AAS can continue to grow and increasingly adapt to the requirements concerning product information and sustainability reporting.
As a result, the Asset Administration Shell creates a fundamental technological foundation that supports the digital product passport through standardized data architectures, optimized interoperability, increased transparency, and the promotion of sustainability goals. In this respect, it is becoming an essential element in the realization of the vision of holistic, digital life cycle management for products.
Sustainability and Carbon Footprint: What Might a Circular Economy Based on Asset Administration Shells Look Like?
In the context of climate change, sustainability is no longer just a desirable goal, but a necessity. As a result, the concept of a circular economy is becoming increasingly important.
The circular economy represents a fundamental shift away from the traditional, linear economy to a regenerative system aimed at minimizing waste and maximizing the reuse of resources.
Within this framework, reducing the carbon footprint is of central importance. The Asset Administration Shell offers innovative solutions for this by using special submodels for the measurement and interoperable exchange of carbon emissions. One example of a practical application is the battery passport – a tool used to document and share the product carbon footprint over the entire life cycle of a product.
The challenge for many companies is to accurately determine a product’s carbon footprint. Different methods of data collection are often used within different areas of the company, which makes it difficult to collect consistent and standardized data. Using Asset Administration Shells to implement a standardized procedure can help to effectively address this issue. This solution not only simplifies carbon footprint monitoring, but also promotes interoperability between all stakeholders, thus supporting a seamless transition to a more sustainable economy.
MHP has extensive expertise when it comes to implementing AAS. We help you effectively achieve your sustainability goals and make a significant contribution to the circular economy. Read our white papers on Zero Impact Products and Circularity Assessment to find out more about our expertise.
The Benefits of AAS at a Glance
What makes the Asset Administration Shell so groundbreaking? The AAS facilitates seamless integration and communication between machines, equipment, and IT systems, and serves as an enabler for real-time data transmission, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, all of which work together on a unified platform. In addition, AAS can facilitate the exchange of information over the entire life cycle of an asset on the basis of uniform and standardized semantics. Information about the entire life cycle – from creation and production to use, maintenance, repair, disposal, or recycling – is collected, updated and shared. Applications that use Asset Administration Shells can be developed, integrated, scaled and used in a standardized way.
This opens up opportunities to optimize processes, realize innovative business models and increase production efficiency. Current issues, such as sustainability in industry, can be managed by implementing the Asset Administration Shell. For companies that want to be at the forefront of technological innovation, implementing an AAS represents an important part of digitizing their assets.
Other benefits of the Asset Administration Shell:
- Facilitated Plug & Produce of devices: Standardizing communication interfaces facilitates the Plug & Produce of devices in production.
- Reduced shop floor expenses: Data standardization also significantly reduces the resources required on the shop floor for planning, commissioning, and operation.
- Use of existing standards: Thanks to AAS, existing standards such as OPC UA can continue to be used and all information from devices in production can be comprehensively mapped in real time, even without a direct data connection.
- High flexibility and scalability: Another significant advantage is the ability to exchange devices with standardized models, regardless of manufacturer. This helps to ensure high flexibility and scalability in production.
- No manual mapping of data points: The information is already stored in the Asset Administration Shell, which reduces the amount of implementation work required and increases efficiency.
Challenges When it Comes to Adopting AAS
While the implementation of the Asset Administration Shell offers significant benefits for the digital life cycle management of products, the transition necessitates considering both initial and ongoing challenges in great detail.
High initial investment and staff training
Introducing AAS involves a significant initial investment in terms of funding, time, and resources. The complexity of this endeavor requires careful planning, and staff training may be required to ensure seamless integration with existing systems.
Data security and protection
Data security and protection is another critical aspect. Given the processing and storage of sensitive information, specific safeguards must be implemented to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
Other challenges
In addition to the challenges listed above, standardization remains a hurdle for many companies – especially given the need to harmonize divergent industry standards and requirements. In addition, the AAS requires regular maintenance and updates to ensure its continued effectiveness and safety, resulting in additional running costs.
Despite these challenges, investing in AAS is a strategic decision that will pay off for companies in the long run. The implementation of comprehensive digital life cycle management enables not only the optimization of operational processes, but also a significant increase in competitiveness.
With the right partner, you can effectively overcome the challenges associated with AAS. Working with MHP will make it easier for your company to implement AAS. Talk to our experts now to find out more!
MHP Is Guiding Businesses into the Future with Asset Administration Shells and Cloud Technologies
In the dynamic world of Industry 4.0, the Asset Administration Shell (AAS) plays a crucial role in advancing digital transformation to the next level. It is not just a technical concept but serves as a bridge between physical assets and the digital world, integrating standardized data models, semantic descriptions, and secure communication protocols.
Together with MHP, you can develop advanced digitalization strategies for your assets, built upon the use of Asset Administration Shells. A key element in this implementation is the plug-and-produce principle, which facilitates the integration of new systems into your production landscape. MHP brings extensive experience in applying this principle and guides companies on their journey toward full adoption.
The synergies between Asset Administration Shells and cloud technologies like AWS offer significant advantages. AWS enables the scalability and flexibility of AAS implementations by adjusting computing power and storage resources as needed. Moreover, integrating with AWS services enhances the security and availability of digital twins, which is essential for continuous operation and real-time analysis. With the AWS cloud, companies can manage their asset data globally and securely, ensuring seamless integration across different locations. Our goal is to extend the use of AAS throughout the entire lifecycle of an asset, leveraging the synergies with cloud technologies like AWS to efficiently scale digital asset strategies. Contact us to learn how we can implement Asset Administration Shells for your company.
Frequently Asked Questions About Asset Administration Shells
The Asset Administration Shell (AAS) is the digital equivalent of a physical object or system. It standardizes all the relevant data and services for sharing information. It facilitates efficient and secure communication between stakeholders and IT systems throughout the entire life cycle of the asset, and thus supports digitalization efforts in the industry by providing a structured and machine-readable database.
The Asset Administration Shell promotes digitalization in production through standardized data exchange and improved communication, resulting in optimized processes, increased efficiency and new business models. It also supports Plug & Produce for flexible production.
MHP supports the development of digitalization strategies for your assets through the use of Asset Administration Shells, including passive, reactive and proactive approaches. We work to establish an efficient production system by gaining the commitment of all parties involved to the Plug & Produce principle and through the experience of our experts. And we make sure that the AAS is applied to the entire life cycle of an asset, going far beyond the entire operational area.